Formation of Halogen Bond-Based 2D Supramolecular Assemblies by Electric Manipulation
Qing-Na Zheng, Xuan-He Liu, Ting Chen, Hui-Juan Yan, Timothy Cook, Dong Wang,*,Peter J. Stang, and Li-Jun Wan*
J. Am. Chem. Soc., Article ASAP DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5b02206
ABSTRACT: Halogen bonding has attracted much attention recently as an important driving force for supramolecular assembly and crystal engineering. Herein, we demonstrate for the first time the formation of a halogen bond-based open porous network on a graphite surface using ethynylpyridine and aryl-halide based building blocks. We found that the electrical stimuli of a scanning tunneling microscopy (STM) tip can induce the formation of a binary supramolecular structure on the basis of halogen bond formation between terminal pyridyl groups and perfluoro-iodobenzene. This electrical manipulation method can be applied to engineer a series of linear or porous structures by selecting halogen bond donor and acceptor fragments with different symmetries, as the directional interactions ultimately determine the structural outcome.
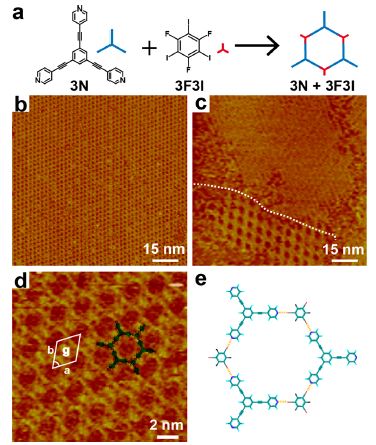
Figure 1. (a) Self-assembly of tritopic XB acceptor 3N and XB donor 3F3I results in the formation of a 3N/3F3I honeycomb structure. (b) Large-scale STM image of the 3N/3F3I honeycomb structure. Tunneling conditions: Vbias = 800 mV, It = 560 pA. (c) The STM image shows the coexistence of a 3N close-packed structure and the 3N/ 3F3I network. Tunneling conditions: Vbias = 770 mV, It = 438 pA. (d) High-resolution STM image of the 3N/3F3I honeycomb structure. Tunneling conditions: Vbias = 888 mV, It = 1060 pA. (e) Structural model of the 3N/3F3I honeycomb structure. Possible XBs are depicted by yellow dashed lines.
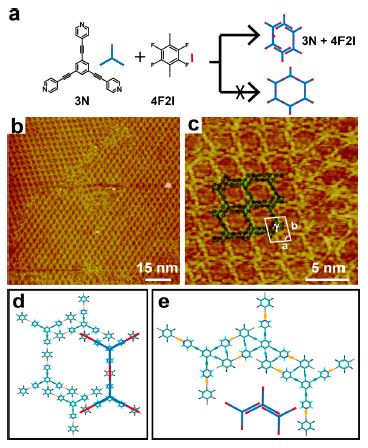
Figure 2. (a) Schematic diagram of the 3N/4F2I self-assembled porous structure. (b) Large-scale STM image of the 3N/4F2I porous structure. Tunneling conditions: Vbias = 679 mV, It = 450 pA. (c) High-resolution STM image of the 3N/4F2I porous structure. Tunneling conditions: Vbias = 725 mV, It = 545 pA. (d) Structural model of the 3N/4F2I porous structure. (e) Details of the 3N/4F2I porous structure. The hydrogen bonds are schematically represented by blue spots. The XBs are schematically represented by yellow spots.
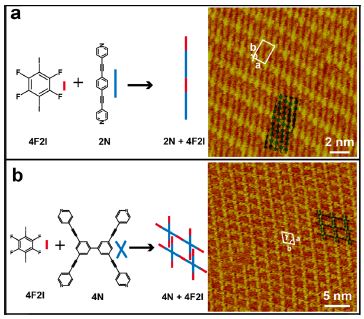
Figure 3. Formation of a series of binary XB-based supramolecular structures between the 4F2I ditopic donor and other XB acceptors. (a) The formation of a 2N/4F2I XB-based linear structure. High-resolution STM image of the 2N/4F2I linear structure. Tunneling conditions: Vbias = 758 mV, It = 513 pA. (b) The formation of the 4N/4F2I XB-based porous structure. High-resolution STM image of the 4N/4F2I porous structure. Tunneling conditions: Vbias = 766 mV, It = 452 pA.

