Yun Zhang, Wen-Jie Jiang, Xing Zhang, Lin Guo, Jin-Song Hu, Zidong Wei, Li-Jun Wan
Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2014, 16, 13605-13609, DOI: 10.1039/C4CP00757C
http://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2014/cp/c4cp00757c#!divAbstract
Abstract (click image for pdf file)
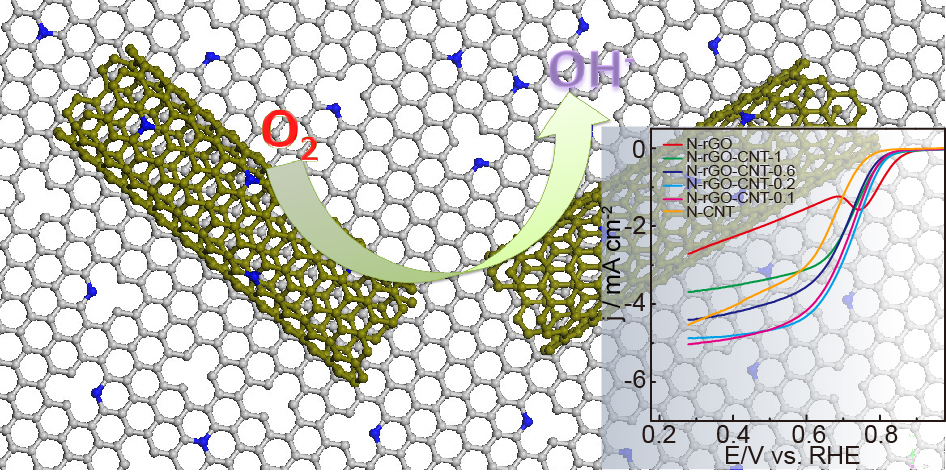
The importance of oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) in fuel cells and high energy density metal-air batteries has attracted intense research interests in looking for low-cost ORR catalysts as substitutes for expensive and scarce Pt-based catalysts. N-doped graphene and carbon nanotubes prepared in a low-cost and scalable way has demonstrated their potentials although the performance still needs to be improved. In view of the requirements for a high-performance ORR electrocatalyst, this work focused on developing the nanocomposites of N-doped reduced graphene oxide (N-rGO) and N-doped carbon nanotubes (N-CNT) as low-cost efficient ORR catalysts by integrating the advantages of abundant highly-active sites from N-rGO and three-dimensional conductive network for efficient mass and electron transport from N-CNT. By optimizing the preparation method and dedicatedly tuning the composition, the much enhanced ORR activity and superior durability and tolerance to methanol were achieved for self-assembled N-doped composite (N-rGO-CNT) at a mass ratio of 1:5 rGO/CNT. The further improvement of ORR electrocatalytic activity of the composite was also demonstrated by introducing iron into the composite.

