Yan Jiang , Xing Zhang , Qian-Qing Ge , Bin-Bin Yu , Yu-Gang Zou , Wen-Jie Jiang , Wei-Guo Song *, Li-Jun Wan *, and Jin-Song Hu *
Nano Lett., 2014, 14, 365-372, DOI: 10.1021/nl404251p, Publication Date (Web): December 13, 2013
http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/nl404251p
Abstract (click image for pdf file)
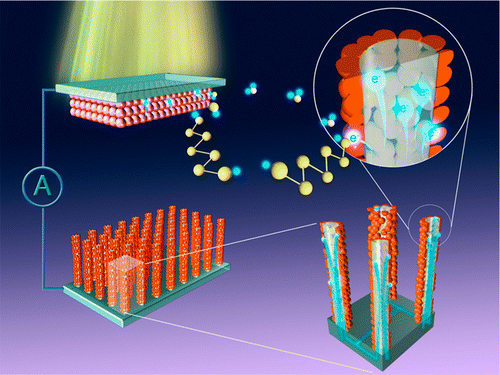
Quantum-dot-sensitized solar cell (QDSSC) has been considered as an alternative to new generation photovoltaics, but it still presents very low power conversion efficiency. Besides the continuous effort on improving photoanodes and electrolytes, the focused investigation on charge transfer at interfaces and the rational design for counter electrodes (CEs) are recently receiving much attention. Herein, core–shell nanowire arrays with tin-doped indium oxide (ITO) nanowire core and Cu2S nanocrystal shell (ITO@Cu2S) were dedicatedly designed and fabricated as new efficient CEs for QDSSCs in order to improve charge collection and transport and to avoid the intrinsic issue of copper dissolution in popular and most efficient Cu/Cu2S CEs. The high-quality tunnel junctions formed between n-type ITO nanowires and p-type Cu2S nanocrystals led to the considerable decrease in sheet resistance and charge transfer resistance and thus facilitated the electron transport during the operation of QDSSCs. The three-dimensional structure of nanowire arrays provided high surface area for more active catalytic sites and easy accessibility for an electrolyte. As a result, the power conversion efficiency of QDSSCs with the designed ITO@Cu2S CEs increased by 84.5 and 33.5% compared to that with planar Au and Cu2S CEs, respectively.

